Page 162 - Petelin, Ana. 2021. Ed. Zdravje starostnikov / Health of the Elderly. Proceedings. Koper: University of Primorska Press.
P. 162
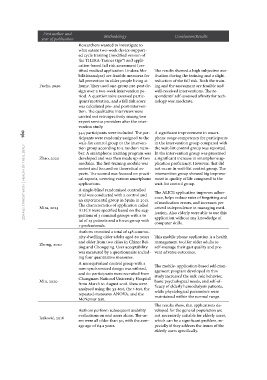
First author and Methodology Conclusion/Results
year of publication
Fuchs, 2020 Researchers wanted to investigate to
what extent two-week device-support-
Zhao, 2020 ed cycle training (modified version of
the THERA-Trainer tigo®) and appli-
Mira, 2014 cation-based fall risk assessment (cer-
Zhong, 2020 tified medical application Lindera Mo- The results showed a high subjective mo-
Min, 2020 bilitätsanalyse) are feasible measures for tivation during the training and a slight
Isaković, 2016 fall prevention in older people living at reduction of the fall risk. Both the train-
home. They used one-group pre-post de- ing and the assessment are feasible and
sign over a two-week intervention pe- well-received interventions. The re-
riod. A questionnaire assessed partic- spondents‘ self-assessed affinity for tech-
ipants’motivation, and a fall risk score nology was moderate.
was calculated pre- and post-interven-
tion. The qualitative interviews were
carried out retrospectively among two
expert service providers after the inter-
vention study.
zdravje starostnikov | health of the elderly 160 344 participants were included. The par- A significant improvement in smart-
ticipants were randomly assigned to the phone usage competency for participants
wait-list control group or the interven- in the intervention group compared with
tion group according to a random num- the wait-list control group was reported.
ber. A smartphone training program was In the intervention group was presented
developed and was then made up of two a significant increase in smartphone ap-
modules. The first training module was plication proficiency. However, that did
easiest and focused on theoretical as- not occur in wait-list control group. The
pects. The second was focused on practi- intervention group showed big improve-
cal aspects, covering various smartphone ment in quality of life compared to the
applications. wait-list control group.
A single-blind randomized controlled The ALICE application improves adher-
trial was conducted with a control and ence, helps reduce rates of forgetting and
an experimental group in Spain in 2013. of medication errors, and increases per-
The characteristics of application called ceived independence in managing med-
ALICE were specified based on the sug- ication. Also elderly were able to use this
gestions of 3 nominal groups with a to- application without any knowledge of
tal of 23 patients and a focus group with computer skills.
7 professionals.
Authors recruited a total of 148 commu- This mobile phone application is a health
nity-dwelling older adults aged 60 years management tool for older adults to
and older from two cities in China: Bei- self-manage their gait quality and pre-
jing and Chongqing. User acceptability vent adverse outcomes.
was measured by a questionnaire includ-
ing four quantitative measures.
A nonequivalent control group with a The mobile- application-based self-man-
non-synchronized design was utilized, agement program developed in this
and 60 participants were recruited from study increased the sick-role behavior,
Chungnam National University Hospital basic psychological needs, and self-ef-
from March to August 2018. Data were ficacy of elderly hemodialysis patients,
analysed using the χ2-test, the t-test, the while physiological parameters were
repeated-measures ANOVA, and the maintained within the normal range.
McNemar test.
Authors perform subsequent usability The results show, that applications de-
evaluations on end users alone. The us- veloped for the general population are
ers were all older than 50, with the aver- not necessarily suitable for elderly users,
age age of 64.2 years. which can be a significant problem, es-
pecially if they address the issues of the
elderly users specifically.
year of publication
Fuchs, 2020 Researchers wanted to investigate to
what extent two-week device-support-
Zhao, 2020 ed cycle training (modified version of
the THERA-Trainer tigo®) and appli-
Mira, 2014 cation-based fall risk assessment (cer-
Zhong, 2020 tified medical application Lindera Mo- The results showed a high subjective mo-
Min, 2020 bilitätsanalyse) are feasible measures for tivation during the training and a slight
Isaković, 2016 fall prevention in older people living at reduction of the fall risk. Both the train-
home. They used one-group pre-post de- ing and the assessment are feasible and
sign over a two-week intervention pe- well-received interventions. The re-
riod. A questionnaire assessed partic- spondents‘ self-assessed affinity for tech-
ipants’motivation, and a fall risk score nology was moderate.
was calculated pre- and post-interven-
tion. The qualitative interviews were
carried out retrospectively among two
expert service providers after the inter-
vention study.
zdravje starostnikov | health of the elderly 160 344 participants were included. The par- A significant improvement in smart-
ticipants were randomly assigned to the phone usage competency for participants
wait-list control group or the interven- in the intervention group compared with
tion group according to a random num- the wait-list control group was reported.
ber. A smartphone training program was In the intervention group was presented
developed and was then made up of two a significant increase in smartphone ap-
modules. The first training module was plication proficiency. However, that did
easiest and focused on theoretical as- not occur in wait-list control group. The
pects. The second was focused on practi- intervention group showed big improve-
cal aspects, covering various smartphone ment in quality of life compared to the
applications. wait-list control group.
A single-blind randomized controlled The ALICE application improves adher-
trial was conducted with a control and ence, helps reduce rates of forgetting and
an experimental group in Spain in 2013. of medication errors, and increases per-
The characteristics of application called ceived independence in managing med-
ALICE were specified based on the sug- ication. Also elderly were able to use this
gestions of 3 nominal groups with a to- application without any knowledge of
tal of 23 patients and a focus group with computer skills.
7 professionals.
Authors recruited a total of 148 commu- This mobile phone application is a health
nity-dwelling older adults aged 60 years management tool for older adults to
and older from two cities in China: Bei- self-manage their gait quality and pre-
jing and Chongqing. User acceptability vent adverse outcomes.
was measured by a questionnaire includ-
ing four quantitative measures.
A nonequivalent control group with a The mobile- application-based self-man-
non-synchronized design was utilized, agement program developed in this
and 60 participants were recruited from study increased the sick-role behavior,
Chungnam National University Hospital basic psychological needs, and self-ef-
from March to August 2018. Data were ficacy of elderly hemodialysis patients,
analysed using the χ2-test, the t-test, the while physiological parameters were
repeated-measures ANOVA, and the maintained within the normal range.
McNemar test.
Authors perform subsequent usability The results show, that applications de-
evaluations on end users alone. The us- veloped for the general population are
ers were all older than 50, with the aver- not necessarily suitable for elderly users,
age age of 64.2 years. which can be a significant problem, es-
pecially if they address the issues of the
elderly users specifically.