Page 39 - Petelin, Ana. 2021. Ed. Zdravje starostnikov / Health of the Elderly. Proceedings. Koper: University of Primorska Press.
P. 39
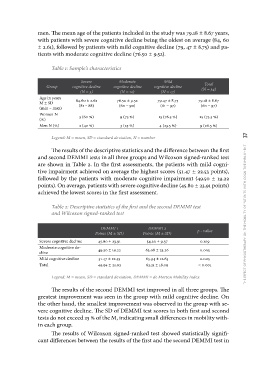
. The mean age of the patients included in the study was 79.18 ± 8.67 years,
with patients with severe cognitive decline being the oldest on average (84, 60
± 2.61), followed by patients with mild cognitive decline (79, 47 ± 8.75) and pa-
tients with moderate cognitive decline (76.50 ± 9.52).
Table 1: Sample’s characteristics
Group Severe Moderate Mild Total
cognitive decline cognitive decline cognitive decline (N = 34)
Age in years
M ± SD (N = 5) (N = 12) (N = 17) 79.18 ± 8.67
(min – max) (60 – 97)
Women N 84.60 ± 2.61 76.50 ± 9.52 79.47 ± 8.75
(%) (81 – 88) (60 – 90) (61 – 97) 25 (73.5 %)
Men N (%) 9 (26.5 %)
3 (60 %) 9 (75 %) 13 (76.5 %)
2 (40 %) 3 (25 %) 4 (23.5 %)
Legend: M = mean, SD = standard deviation, N = number the effect of physiotherapy on the mobility of patients with cognitive impairment 37
The results of the descriptive statistics and the difference between the first
and second DEMMI tests in all three groups and Wilcoxon signed-ranked test
are shown in Table 2. In the first assessments, the patients with mild cogni-
tive impairment achieved on average the highest scores (51.47 ± 22.53 points),
followed by the patients with moderate cognitive impairment (49.50 ± 19.22
points). On average, patients with severe cognitive decline (45.80 ± 23.91 points)
achieved the lowest scores in the first assessment.
Table 2: Descriptive statistics of the first and the second DEMMI test
and Wilcoxon signed-ranked test
Severe cognitive decline DEMMI 1 DEMMI 2 p - value
Moderate cognitive de- Points (M ± SD) Points (M ± SD)
cline 0.109
Mild cognitive decline 45.80 ± 23.91 54.20 ± 9.37 0.005
Total 0.005
49.50 ± 19.22 63.08 ± 23.26 < 0.001
51.47 ± 22.53 65.94 ± 12.65
49.94 ± 21.03 63.21 ± 18.09
Legend: M = mean, SD = standard deviation, DEMMI = de Morton Mobility Index
The results of the second DEMMI test improved in all three groups. The
greatest improvement was seen in the group with mild cognitive decline. On
the other hand, the smallest improvement was observed in the group with se-
vere cognitive decline. The SD of DEMMI test scores in both first and second
tests do not exceed 25 % of the M, indicating small differences in mobility with-
in each group.
The results of Wilcoxon signed-ranked test showed statistically signifi-
cant differences between the results of the first and the second DEMMI test in
with patients with severe cognitive decline being the oldest on average (84, 60
± 2.61), followed by patients with mild cognitive decline (79, 47 ± 8.75) and pa-
tients with moderate cognitive decline (76.50 ± 9.52).
Table 1: Sample’s characteristics
Group Severe Moderate Mild Total
cognitive decline cognitive decline cognitive decline (N = 34)
Age in years
M ± SD (N = 5) (N = 12) (N = 17) 79.18 ± 8.67
(min – max) (60 – 97)
Women N 84.60 ± 2.61 76.50 ± 9.52 79.47 ± 8.75
(%) (81 – 88) (60 – 90) (61 – 97) 25 (73.5 %)
Men N (%) 9 (26.5 %)
3 (60 %) 9 (75 %) 13 (76.5 %)
2 (40 %) 3 (25 %) 4 (23.5 %)
Legend: M = mean, SD = standard deviation, N = number the effect of physiotherapy on the mobility of patients with cognitive impairment 37
The results of the descriptive statistics and the difference between the first
and second DEMMI tests in all three groups and Wilcoxon signed-ranked test
are shown in Table 2. In the first assessments, the patients with mild cogni-
tive impairment achieved on average the highest scores (51.47 ± 22.53 points),
followed by the patients with moderate cognitive impairment (49.50 ± 19.22
points). On average, patients with severe cognitive decline (45.80 ± 23.91 points)
achieved the lowest scores in the first assessment.
Table 2: Descriptive statistics of the first and the second DEMMI test
and Wilcoxon signed-ranked test
Severe cognitive decline DEMMI 1 DEMMI 2 p - value
Moderate cognitive de- Points (M ± SD) Points (M ± SD)
cline 0.109
Mild cognitive decline 45.80 ± 23.91 54.20 ± 9.37 0.005
Total 0.005
49.50 ± 19.22 63.08 ± 23.26 < 0.001
51.47 ± 22.53 65.94 ± 12.65
49.94 ± 21.03 63.21 ± 18.09
Legend: M = mean, SD = standard deviation, DEMMI = de Morton Mobility Index
The results of the second DEMMI test improved in all three groups. The
greatest improvement was seen in the group with mild cognitive decline. On
the other hand, the smallest improvement was observed in the group with se-
vere cognitive decline. The SD of DEMMI test scores in both first and second
tests do not exceed 25 % of the M, indicating small differences in mobility with-
in each group.
The results of Wilcoxon signed-ranked test showed statistically signifi-
cant differences between the results of the first and the second DEMMI test in