Page 15 - Fister jr., Iztok, Andrej Brodnik, Matjaž Krnc and Iztok Fister (eds.). StuCoSReC. Proceedings of the 2019 6th Student Computer Science Research Conference. Koper: University of Primorska Press, 2019
P. 15
munication Image capture
subsystem and processing
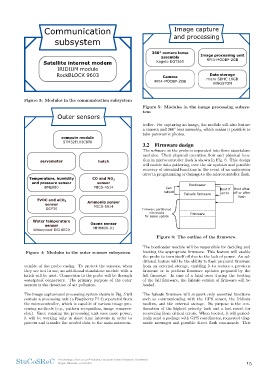
Satellite internet modem 360° camera lense Image processing unit
IRIDIUM module assembly RPI4-MODBP-2GB
RockBLOCK 9603
Kogeto DOT360 Data storage
micro SDHC 16GB
Camera
RPI4-MODBP-2GB KINGSTON
Figure 3: Modules in the communication subsystem Figure 5: Modules in the image processing subsys-
tem
Outer sensors
troller. For capturing an image, the module will also feature
a camera and 360◦ lens assembly, which makes it possible to
take panoramic photos.
compute module 3.2 Firmware design
STM32F103C8T6
The software on the probe is separated into three standalone
servomotor hatch modules. Their physical execution flow and physical loca-
tion in microcontroller flash is shown in Fig. 6. This design
will enable data gathering, over the air updates and possible
recovery of essential functions in the event of an unforeseen
error in programming or damage to the microcontroller flash.
Temperature, humidity CO and NO2 Can Bootloader Boot if Boot after
and pressure sensor sensor reboot Failsafe firmware error off or after
BME680
MICS-4514 flash
TVOC and eCO2
sensor Ammonia sensor Firmware partitioned Firmware
SGP30 MICS-5914 into blocks
Water temperature Ozone sensor for easier update
sensor MHM400-01
Waterproof DS18B20
Figure 4: Modules in the outer sensors subsystem Figure 6: The outline of the firmware.
outside of the probe casing. To protect the sensors, when The bootloader module will be responsible for deciding and
they are not in use, an additional standalone module with a booting the appropriate firmware. This feature will enable
hatch will be used. Connection to the probe will be through the probe to turn itself off due to the lack of power. An ad-
waterproof connectors. The primary purpose of the outer ditional feature will be the ability to flash prepared firmware
sensors is the detection of air pollution. from an external storage, enabling it to restore a previous
firmware or to perform firmware updates prepared by the
The image capture and processing system shown in Fig. 5 wil full firmware. In case of a fatal error during the booting
contain a processing unit (a Raspberry Pi 4) separated from of the full firmware, the failsafe version of firmware will be
the microcontroller, which is capable of various image pro- loaded.
cessing methods (e.g., pattern recognition, image compres-
sion). Since running the processing unit uses more power, The failsafe firmware will support only essential functions
it will be working only in short time intervals in order to such as communicating with the GPS sensor, the Iridium
process and transfer the needed data to the main microcon- modem, and the external storage. Its purpose is the con-
tinuation of the highest priority task and a last resort for
recovering from critical errors. When booted, it will period-
ically send a package with GPS coordinates, requested diag-
nostic messages and possible direct flash commands. This
StuCoSReC Proceedings of the 2019 6th Student Computer Science Research Conference 15
Koper, Slovenia, 10 October
subsystem and processing
Satellite internet modem 360° camera lense Image processing unit
IRIDIUM module assembly RPI4-MODBP-2GB
RockBLOCK 9603
Kogeto DOT360 Data storage
micro SDHC 16GB
Camera
RPI4-MODBP-2GB KINGSTON
Figure 3: Modules in the communication subsystem Figure 5: Modules in the image processing subsys-
tem
Outer sensors
troller. For capturing an image, the module will also feature
a camera and 360◦ lens assembly, which makes it possible to
take panoramic photos.
compute module 3.2 Firmware design
STM32F103C8T6
The software on the probe is separated into three standalone
servomotor hatch modules. Their physical execution flow and physical loca-
tion in microcontroller flash is shown in Fig. 6. This design
will enable data gathering, over the air updates and possible
recovery of essential functions in the event of an unforeseen
error in programming or damage to the microcontroller flash.
Temperature, humidity CO and NO2 Can Bootloader Boot if Boot after
and pressure sensor sensor reboot Failsafe firmware error off or after
BME680
MICS-4514 flash
TVOC and eCO2
sensor Ammonia sensor Firmware partitioned Firmware
SGP30 MICS-5914 into blocks
Water temperature Ozone sensor for easier update
sensor MHM400-01
Waterproof DS18B20
Figure 4: Modules in the outer sensors subsystem Figure 6: The outline of the firmware.
outside of the probe casing. To protect the sensors, when The bootloader module will be responsible for deciding and
they are not in use, an additional standalone module with a booting the appropriate firmware. This feature will enable
hatch will be used. Connection to the probe will be through the probe to turn itself off due to the lack of power. An ad-
waterproof connectors. The primary purpose of the outer ditional feature will be the ability to flash prepared firmware
sensors is the detection of air pollution. from an external storage, enabling it to restore a previous
firmware or to perform firmware updates prepared by the
The image capture and processing system shown in Fig. 5 wil full firmware. In case of a fatal error during the booting
contain a processing unit (a Raspberry Pi 4) separated from of the full firmware, the failsafe version of firmware will be
the microcontroller, which is capable of various image pro- loaded.
cessing methods (e.g., pattern recognition, image compres-
sion). Since running the processing unit uses more power, The failsafe firmware will support only essential functions
it will be working only in short time intervals in order to such as communicating with the GPS sensor, the Iridium
process and transfer the needed data to the main microcon- modem, and the external storage. Its purpose is the con-
tinuation of the highest priority task and a last resort for
recovering from critical errors. When booted, it will period-
ically send a package with GPS coordinates, requested diag-
nostic messages and possible direct flash commands. This
StuCoSReC Proceedings of the 2019 6th Student Computer Science Research Conference 15
Koper, Slovenia, 10 October