Page 18 - Petelin, Ana. 2021. Ed. Zdravje starostnikov / Health of the Elderly. Proceedings. Koper: University of Primorska Press.
P. 18
Twelve articles included in the systematic review of the literature met all
the set inclusion criteria. Articles that were in line with the purpose and goal of
our systematic review were evaluated with a Measurement Tool to Assess sys-
tematic review (AMSTAR) (Table 2). A total of 5,978 patients participated in all
studies included in our review. The PRISMA approach () was used to show the
course of the literature review (Figure 1) (Moher et al., 2015). We further im-
ported the results into the Zotero program, which is a research tool that also
enables the organization, storage of resources, management and citation of our
references.
zdravje starostnikov | health of the elderly 16 Results
We identified and analysed 12 articles (Ueda et al., 2013; Ing-Randolph et al.,
2015; Fusar-Poli et al., 2018; Gomez-Romero et al., 2017; Sherriff et al., 2017;
Rezende Alexio et al., 2017; Zhang et al., 2016; Mercadal-Brotons and Alcanta-
ra-Silva., 2019; Bartfy et al., 2019; Li et al., 2019; Long Lam et al., 2020; Morales
et al., 2020) showed on (Table 2).
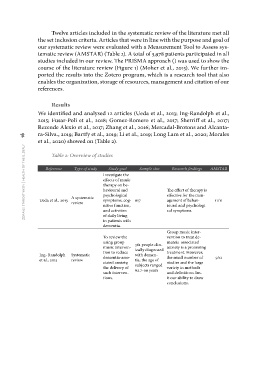
Table 2: Overview of studies
Reference Type of study Study goal Sample size Research findings AMSTAR
Investigate the 617 The effect of therapy is 11/11
Ueda et al., 2013 A systematic effects of music 361 people clin- effective for the man-
review therapy on be- ically diagnosed agement of behav- 9/11
havioural and with demen- ioural and psychologi-
Ing- Randolph Systematic psychological tia, the age of cal symptoms.
et al., 2015 review symptoms, cog- subjects ranged Group music inter-
nitive function, 62.7-99 years vention to treat de-
and activities mentia-associated
of daily living anxiety is a promising
in patients with treatment. However,
dementia. the small number of
studies and the large
To review the variety in methods
using group and definitions lim-
music interven- it our ability to draw
tion to reduce conclusions.
dementia-asso-
ciated anxiety,
the delivery of
such interven-
tions.
the set inclusion criteria. Articles that were in line with the purpose and goal of
our systematic review were evaluated with a Measurement Tool to Assess sys-
tematic review (AMSTAR) (Table 2). A total of 5,978 patients participated in all
studies included in our review. The PRISMA approach () was used to show the
course of the literature review (Figure 1) (Moher et al., 2015). We further im-
ported the results into the Zotero program, which is a research tool that also
enables the organization, storage of resources, management and citation of our
references.
zdravje starostnikov | health of the elderly 16 Results
We identified and analysed 12 articles (Ueda et al., 2013; Ing-Randolph et al.,
2015; Fusar-Poli et al., 2018; Gomez-Romero et al., 2017; Sherriff et al., 2017;
Rezende Alexio et al., 2017; Zhang et al., 2016; Mercadal-Brotons and Alcanta-
ra-Silva., 2019; Bartfy et al., 2019; Li et al., 2019; Long Lam et al., 2020; Morales
et al., 2020) showed on (Table 2).
Table 2: Overview of studies
Reference Type of study Study goal Sample size Research findings AMSTAR
Investigate the 617 The effect of therapy is 11/11
Ueda et al., 2013 A systematic effects of music 361 people clin- effective for the man-
review therapy on be- ically diagnosed agement of behav- 9/11
havioural and with demen- ioural and psychologi-
Ing- Randolph Systematic psychological tia, the age of cal symptoms.
et al., 2015 review symptoms, cog- subjects ranged Group music inter-
nitive function, 62.7-99 years vention to treat de-
and activities mentia-associated
of daily living anxiety is a promising
in patients with treatment. However,
dementia. the small number of
studies and the large
To review the variety in methods
using group and definitions lim-
music interven- it our ability to draw
tion to reduce conclusions.
dementia-asso-
ciated anxiety,
the delivery of
such interven-
tions.