Page 19 - Petelin, Ana. 2021. Ed. Zdravje starostnikov / Health of the Elderly. Proceedings. Koper: University of Primorska Press.
P. 19
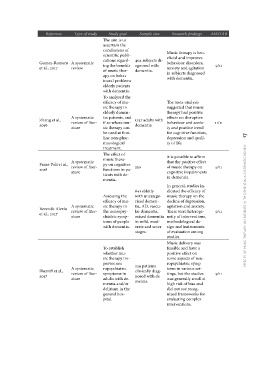
erence Type of study Study goal Sample size Research findings AMSTAR
Gomez-Romero A systematic The aim is to 404 subjects di- Music therapy is ben- 9/11
et al., 2017 review ascertain the agnosed with eficial and improves
conclusions of dementia. behaviour disorders,
scientific publi- anxiety and agitation
cations regard- in subjects diagnosed
ing the benefits with dementia.
of music ther-
apy on behav-
ioural problems
elderly patients
with dementia.
Zhang et al., A systematic To analysed the 1757 adults with The meta-analysis 11/11
2016 review of liter- efficacy of mu- dementia suggested that music
ature sic therapy in therapy had positive
elderly demen- effects on disruptive
tia patients, and behaviour and anxie- effects of music therapy on patients with dementia: a systematic review 17
if so where mu- ty and positive trend
sic therapy can for cognitive function,
be used at first- depression and quali-
line non-phar- ty of life.
macological
treatment.
The effect of It is possible to affirm
music thera- that the positive effect
Fusar-Poli et al., A systematic py on cognitive of music therapy on
2018 review of liter- functions in pa- 330 cognitive impairments 9/11
ature in dementia.
tients with de-
mentia.
641 elderly In general, studies in-
dicated the efficacy of
Assessing the with uncatego- music therapy on the
efficacy of mu- rized demen- decline of depression,
A systematic sic therapy in tia, AD, vascu- agitation and anxiety.
Rezende Alexio review of liter- the neuropsy- lar dementia, There were heteroge- 9/11
et al., 2017 ature chiatric symp- mixed dementia neity of interventions,
toms of people
with dementia. in mild, mod- methodological de-
erate and sever sign and instruments
stages. of evaluation among
studies.
Sherriff et al., A systematic To establish 239 patients Music delivery was 9/11
2017 review of liter- whether mu- clinically diag- feasible and have a
ature sic therapy im- nosed with de- positive effect on
proves neu- mentia. some aspects of neu-
ropsychiatric ropsychiatric symp-
symptoms in toms in various set-
adults with de- tings, but the studies
mentia and/or was generally small at
delirium in the high risk of bias and
general hos- did not use recog-
pital. nized frameworks for
evaluating complex
interventions.
Gomez-Romero A systematic The aim is to 404 subjects di- Music therapy is ben- 9/11
et al., 2017 review ascertain the agnosed with eficial and improves
conclusions of dementia. behaviour disorders,
scientific publi- anxiety and agitation
cations regard- in subjects diagnosed
ing the benefits with dementia.
of music ther-
apy on behav-
ioural problems
elderly patients
with dementia.
Zhang et al., A systematic To analysed the 1757 adults with The meta-analysis 11/11
2016 review of liter- efficacy of mu- dementia suggested that music
ature sic therapy in therapy had positive
elderly demen- effects on disruptive
tia patients, and behaviour and anxie- effects of music therapy on patients with dementia: a systematic review 17
if so where mu- ty and positive trend
sic therapy can for cognitive function,
be used at first- depression and quali-
line non-phar- ty of life.
macological
treatment.
The effect of It is possible to affirm
music thera- that the positive effect
Fusar-Poli et al., A systematic py on cognitive of music therapy on
2018 review of liter- functions in pa- 330 cognitive impairments 9/11
ature in dementia.
tients with de-
mentia.
641 elderly In general, studies in-
dicated the efficacy of
Assessing the with uncatego- music therapy on the
efficacy of mu- rized demen- decline of depression,
A systematic sic therapy in tia, AD, vascu- agitation and anxiety.
Rezende Alexio review of liter- the neuropsy- lar dementia, There were heteroge- 9/11
et al., 2017 ature chiatric symp- mixed dementia neity of interventions,
toms of people
with dementia. in mild, mod- methodological de-
erate and sever sign and instruments
stages. of evaluation among
studies.
Sherriff et al., A systematic To establish 239 patients Music delivery was 9/11
2017 review of liter- whether mu- clinically diag- feasible and have a
ature sic therapy im- nosed with de- positive effect on
proves neu- mentia. some aspects of neu-
ropsychiatric ropsychiatric symp-
symptoms in toms in various set-
adults with de- tings, but the studies
mentia and/or was generally small at
delirium in the high risk of bias and
general hos- did not use recog-
pital. nized frameworks for
evaluating complex
interventions.