Page 175 - Petelin, Ana, Nejc Šarabon, Boštjan Žvanut, eds. 2017. Zdravje delovno aktivne populacije ▪︎ Health of the Working-Age Population. Proceedings. Koper: Založba Univerze na Primorskem/University of Primorska Press
P. 175
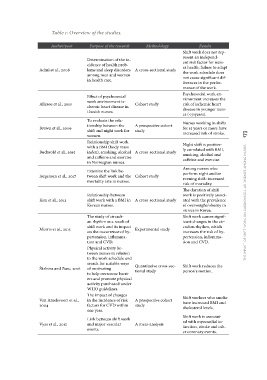
le 1: Overview of the studies.
Author/year Purpose of the research Methodology Results
Admi et al., 2008 Shift work does not rep-
Determination of the in- A cross-sectional study resent an independ-
Allesøe et al., 2010 cidence of health prob- ent risk factor for nurs-
Brown et al., 2009 lems and sleep disorders es health; failure to adapt
Buchvold et al., 2015 among men and women the work schedule does
Jørgensen et al., 2017 in health care. not cause significant dif-
Kim et al., 2013 ferences in the perfor-
Morris et al., 2015 Effect of psychosocial Cohort study mance of the work.
work environment is- Psychosocial work en-
Škrbina and Zurc, 2016 chemic heart disease in vironment increases the
Van Amelsvoort et al., Danish nurses. risk of ischemic heart
2004 disease in younger nurs-
Vyas et al., 2012 To evaluate the rela- es (<51years).
tionship between the A prospective cohort Nurses working in shifts
shift and night work for study for 15 years or more have the impact of shift work on cardiovascular diseases among nurses 173
women. increased risk of stroke.
Night shift is positive-
Relationship shift work ly correlated with BMI,
with a BMI (body mass smoking, alcohol and
index), smoking, alcohol A cross-sectional study caffeine and exercise.
and caffeine and exercise Among nurses who
in Norwegian nurses. perform night and/or
evening shift: increased
Examine the link be- risk of mortality.
tween shift work and the Cohort study The duration of shift
mortality rate in nurses. work is positively associ-
ated with the prevalence
Relationship between of overweight/obesity in
shift work with a BMI in A cross-sectional study nurses in Korea.
Korean nurses. Shift work causes signif-
icant changes in the cir-
The study of circadi- Experimental study cadian rhythm, which
an rhythm as a result of increases the risk of hy-
shift work and its impact pertension, inflamma-
on the occurrence of hy- tion and CVD.
pertension, inflamma-
tion and CVD. Shift work reduces the
person's motion.
Physical activity be-
tween nurses in relation Shift workers who smoke
to the work schedule and have increased BMI and
search for suitable ways sholesterol levels.
of motivating Quantitative cross-sec- Shift work is associat-
to help overcome barri- tional study ed with myocardial in-
farction, stroke and oth-
ers and promote physical er coronary events.
activity purchased under
WHO guidelines.
The impact of changes A prospective cohort
in the incidence of risk study
factors for CVD within
one year.
Link between shift work A meta-analysis
and major vascular
events.
Author/year Purpose of the research Methodology Results
Admi et al., 2008 Shift work does not rep-
Determination of the in- A cross-sectional study resent an independ-
Allesøe et al., 2010 cidence of health prob- ent risk factor for nurs-
Brown et al., 2009 lems and sleep disorders es health; failure to adapt
Buchvold et al., 2015 among men and women the work schedule does
Jørgensen et al., 2017 in health care. not cause significant dif-
Kim et al., 2013 ferences in the perfor-
Morris et al., 2015 Effect of psychosocial Cohort study mance of the work.
work environment is- Psychosocial work en-
Škrbina and Zurc, 2016 chemic heart disease in vironment increases the
Van Amelsvoort et al., Danish nurses. risk of ischemic heart
2004 disease in younger nurs-
Vyas et al., 2012 To evaluate the rela- es (<51years).
tionship between the A prospective cohort Nurses working in shifts
shift and night work for study for 15 years or more have the impact of shift work on cardiovascular diseases among nurses 173
women. increased risk of stroke.
Night shift is positive-
Relationship shift work ly correlated with BMI,
with a BMI (body mass smoking, alcohol and
index), smoking, alcohol A cross-sectional study caffeine and exercise.
and caffeine and exercise Among nurses who
in Norwegian nurses. perform night and/or
evening shift: increased
Examine the link be- risk of mortality.
tween shift work and the Cohort study The duration of shift
mortality rate in nurses. work is positively associ-
ated with the prevalence
Relationship between of overweight/obesity in
shift work with a BMI in A cross-sectional study nurses in Korea.
Korean nurses. Shift work causes signif-
icant changes in the cir-
The study of circadi- Experimental study cadian rhythm, which
an rhythm as a result of increases the risk of hy-
shift work and its impact pertension, inflamma-
on the occurrence of hy- tion and CVD.
pertension, inflamma-
tion and CVD. Shift work reduces the
person's motion.
Physical activity be-
tween nurses in relation Shift workers who smoke
to the work schedule and have increased BMI and
search for suitable ways sholesterol levels.
of motivating Quantitative cross-sec- Shift work is associat-
to help overcome barri- tional study ed with myocardial in-
farction, stroke and oth-
ers and promote physical er coronary events.
activity purchased under
WHO guidelines.
The impact of changes A prospective cohort
in the incidence of risk study
factors for CVD within
one year.
Link between shift work A meta-analysis
and major vascular
events.