Page 240 - Hojnik, Jana. 2017. In Persuit of Eco-innovation. Drivers and Consequences of Eco-innovation at Firm Level. Koper: University of Primorska Press
P. 240
In Pursuit of Eco-innovation
240
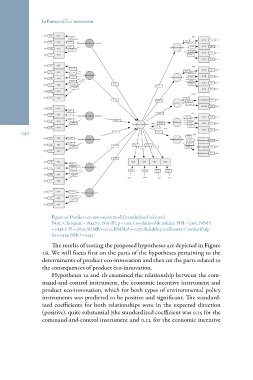
Figure 26: Product eco-innovation model (standardized solution)
Note: Chi-square = 1842.735 (879 df ); p = 0.00; Goodness-of-fit indexes: NFI = 0.763; NNFI
= 0.848; CFI = 0.859; SRMR = 0.212; RMSEA = 0.077; Reliability coefficients: Cronbach’s alp-
ha = 0.939; RHO = 0.947.
The results of testing the proposed hypotheses are depicted in Figure
26. We will focus first on the parts of the hypotheses pertaining to the
determinants of product eco-innovation and then on the parts related to
the consequences of product eco-innovation.
Hypotheses 1a and 1b examined the relationship between the com-
mand-and-control instrument, the economic incentive instrument and
product eco-innovation, which for both types of environmental policy
instruments was predicted to be positive and significant. The standard-
ized coefficients for both relationships were in the expected direction
(positive), quite substantial (the standardized coefficient was 0.15 for the
command-and-control instrument and 0.12 for the economic incentive
240
Figure 26: Product eco-innovation model (standardized solution)
Note: Chi-square = 1842.735 (879 df ); p = 0.00; Goodness-of-fit indexes: NFI = 0.763; NNFI
= 0.848; CFI = 0.859; SRMR = 0.212; RMSEA = 0.077; Reliability coefficients: Cronbach’s alp-
ha = 0.939; RHO = 0.947.
The results of testing the proposed hypotheses are depicted in Figure
26. We will focus first on the parts of the hypotheses pertaining to the
determinants of product eco-innovation and then on the parts related to
the consequences of product eco-innovation.
Hypotheses 1a and 1b examined the relationship between the com-
mand-and-control instrument, the economic incentive instrument and
product eco-innovation, which for both types of environmental policy
instruments was predicted to be positive and significant. The standard-
ized coefficients for both relationships were in the expected direction
(positive), quite substantial (the standardized coefficient was 0.15 for the
command-and-control instrument and 0.12 for the economic incentive