Page 30 - Hojnik, Jana. 2017. In Persuit of Eco-innovation. Drivers and Consequences of Eco-innovation at Firm Level. Koper: University of Primorska Press
P. 30
In Pursuit of Eco-innovation
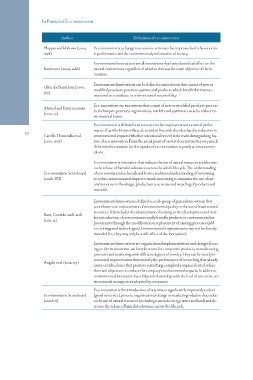
Author Definition of eco-innovation
Huppes and Ishikawa (2009, Eco-innovation is a change in economic activities that improves both the econom-
1698) ic performance and the environmental performance of society.
Kammerer (2009, 2286) Environmental innovations are all innovations that have a beneficial effect on the
natural environment regardless of whether this was the main objective of the in-
novation.
Oltra and Saint Jean (2009, Environmental innovations can be defined as innovations that consist of new or
567) modified processes, practices, systems and products, which benefit the environ-
ment and so contribute to environmental sustainability.
Ahmed and Kamruzzaman Eco-innovations are innovations that consist of new or modified products, process-
(2010, 10) es, techniques, practices, organizations, markets and systems to avoid or reduce en-
vironmental harms.
Eco-innovation is defined as an innovation that improves environmental perfor-
30 Carrillo-Hermosilla et al. mance (Carrillo-Hermosilla et al., 2009), in line with the idea that the reduction in
environmental impacts (whether intentional or not) is the main distinguishing fea-
(2010, 1075) ture of eco-innovation. From the social point of view, it does not matter very much
if the initial motivation for the uptake of eco-innovation is purely an environmen-
tal one.
Eco-innovation Scoreboard Eco-innovation is innovation that reduces the use of natural resources and decreas-
(2011b, VII) es the release of harmful substances across the whole lifecycle. The understanding
of eco-innovation has broadened from a traditional understanding of innovating
to reduce environmental impacts towards innovating to minimize the use of nat-
ural resources in the design, production, use, re-use and recycling of products and
materials.
Rave, Goetzke and Larch Environmental innovation is defined as a sub-group of general innovations that
(2011, 12) contribute to an improvement of environmental quality or the use of fewer natural
resources. This includes the advancement of existing or the development and mar-
Angelo et al. (2012, 117) ket introduction of new environmentally friendly products or environmental im-
provements through the modification or replacement of existing processes (add-
Eco-innovation Scoreboard on or integrated technologies). Environmental improvements may not be directly
(2012b, 8) intended (i.e., they may only be a side effect of the innovation).
Environmental innovations are organizational implementations and changes focus-
ing on the environment, with implications for companies’ products, manufacturing
processes and marketing, with different degrees of novelty. They can be merely in-
cremental improvements that intensify the performance of something that already
exists, or radical ones that promote something completely unprecedented, where
the main objective is to reduce the company’s environmental impacts. In addition,
environmental innovation has a bilateral relationship with the level of pro-active en-
vironmental management adopted by companies.
Eco-innovation is the introduction of any new or significantly improved product
(good or service), process, organizational change or marketing solution that reduc-
es the use of natural resources (including materials, energy, water and land) and de-
creases the release of harmful substances across the lifecycle.
Author Definition of eco-innovation
Huppes and Ishikawa (2009, Eco-innovation is a change in economic activities that improves both the econom-
1698) ic performance and the environmental performance of society.
Kammerer (2009, 2286) Environmental innovations are all innovations that have a beneficial effect on the
natural environment regardless of whether this was the main objective of the in-
novation.
Oltra and Saint Jean (2009, Environmental innovations can be defined as innovations that consist of new or
567) modified processes, practices, systems and products, which benefit the environ-
ment and so contribute to environmental sustainability.
Ahmed and Kamruzzaman Eco-innovations are innovations that consist of new or modified products, process-
(2010, 10) es, techniques, practices, organizations, markets and systems to avoid or reduce en-
vironmental harms.
Eco-innovation is defined as an innovation that improves environmental perfor-
30 Carrillo-Hermosilla et al. mance (Carrillo-Hermosilla et al., 2009), in line with the idea that the reduction in
environmental impacts (whether intentional or not) is the main distinguishing fea-
(2010, 1075) ture of eco-innovation. From the social point of view, it does not matter very much
if the initial motivation for the uptake of eco-innovation is purely an environmen-
tal one.
Eco-innovation Scoreboard Eco-innovation is innovation that reduces the use of natural resources and decreas-
(2011b, VII) es the release of harmful substances across the whole lifecycle. The understanding
of eco-innovation has broadened from a traditional understanding of innovating
to reduce environmental impacts towards innovating to minimize the use of nat-
ural resources in the design, production, use, re-use and recycling of products and
materials.
Rave, Goetzke and Larch Environmental innovation is defined as a sub-group of general innovations that
(2011, 12) contribute to an improvement of environmental quality or the use of fewer natural
resources. This includes the advancement of existing or the development and mar-
Angelo et al. (2012, 117) ket introduction of new environmentally friendly products or environmental im-
provements through the modification or replacement of existing processes (add-
Eco-innovation Scoreboard on or integrated technologies). Environmental improvements may not be directly
(2012b, 8) intended (i.e., they may only be a side effect of the innovation).
Environmental innovations are organizational implementations and changes focus-
ing on the environment, with implications for companies’ products, manufacturing
processes and marketing, with different degrees of novelty. They can be merely in-
cremental improvements that intensify the performance of something that already
exists, or radical ones that promote something completely unprecedented, where
the main objective is to reduce the company’s environmental impacts. In addition,
environmental innovation has a bilateral relationship with the level of pro-active en-
vironmental management adopted by companies.
Eco-innovation is the introduction of any new or significantly improved product
(good or service), process, organizational change or marketing solution that reduc-
es the use of natural resources (including materials, energy, water and land) and de-
creases the release of harmful substances across the lifecycle.