Page 72 - Sember, Vedrana, and Shawnda A. Morrison. 2018. The Mind-Body Connection. Koper: University of Primorska Press.
P. 72
sical Fitness
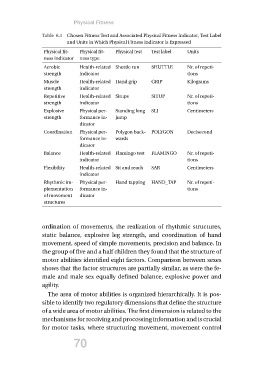
Table 6.1 Chosen Fitness Test and Associated Physical Fitness Indicator, Test Label
and Units in Which Physical Fitness Indicator is Expressed
Physical fit- Physical fit- Physical test Test label Units
ness indicator ness type SHUTTLE
Aerobic GRIP Nr. of repeti-
strength Health-related Shuttle run SITUP tions
Muscle indicator SLJ Kilograms
strength
Repetitive Health-related Hand grip POLYGON Nr. of repeti-
strength indicator tions
Explosive FLAMINGO Centimeters
strength Health-related Situps SAR
indicator HAND_TAP Decisecond
Coordination
Physical per- Standing long Nr. of repeti-
Balance formance in- jump tions
dicator Centimeters
Flexibility
Physical per- Polygon back- Nr. of repeti-
Rhythmic im- formance in- wards tions
plementation dicator
of movement
structures Health-related Flamingo test
indicator
Health-related Sit and reach
indicator
Physical per- Hand tapping
formance in-
dicator
ordination of movements, the realization of rhythmic structures,
static balance, explosive leg strength, and coordination of hand
movement, speed of simple movements, precision and balance. In
the group of five and a half children they found that the structure of
motor abilities identified eight factors. Comparison between sexes
shows that the factor structures are partially similar, as were the fe-
male and male sex equally defined balance, explosive power and
agility.
The area of motor abilities is organized hierarchically. It is pos-
sible to identify two regulatory dimensions that define the structure
of a wide area of motor abilities. The first dimension is related to the
mechanisms for receiving and processing information and is crucial
for motor tasks, where structuring movement, movement control
70
Table 6.1 Chosen Fitness Test and Associated Physical Fitness Indicator, Test Label
and Units in Which Physical Fitness Indicator is Expressed
Physical fit- Physical fit- Physical test Test label Units
ness indicator ness type SHUTTLE
Aerobic GRIP Nr. of repeti-
strength Health-related Shuttle run SITUP tions
Muscle indicator SLJ Kilograms
strength
Repetitive Health-related Hand grip POLYGON Nr. of repeti-
strength indicator tions
Explosive FLAMINGO Centimeters
strength Health-related Situps SAR
indicator HAND_TAP Decisecond
Coordination
Physical per- Standing long Nr. of repeti-
Balance formance in- jump tions
dicator Centimeters
Flexibility
Physical per- Polygon back- Nr. of repeti-
Rhythmic im- formance in- wards tions
plementation dicator
of movement
structures Health-related Flamingo test
indicator
Health-related Sit and reach
indicator
Physical per- Hand tapping
formance in-
dicator
ordination of movements, the realization of rhythmic structures,
static balance, explosive leg strength, and coordination of hand
movement, speed of simple movements, precision and balance. In
the group of five and a half children they found that the structure of
motor abilities identified eight factors. Comparison between sexes
shows that the factor structures are partially similar, as were the fe-
male and male sex equally defined balance, explosive power and
agility.
The area of motor abilities is organized hierarchically. It is pos-
sible to identify two regulatory dimensions that define the structure
of a wide area of motor abilities. The first dimension is related to the
mechanisms for receiving and processing information and is crucial
for motor tasks, where structuring movement, movement control
70