Page 56 - Petelin, Ana, et al. 2019. Eds. Zdravje otrok in mladostnikov / Health of Children and Adolescents. Proceedings. Koper: University of Primorska Press
P. 56
The results showed a statistically significant correlation between the
above-mentioned indicators and the frequency of performance of OGDP as
well as between them and the duration of OGDP.
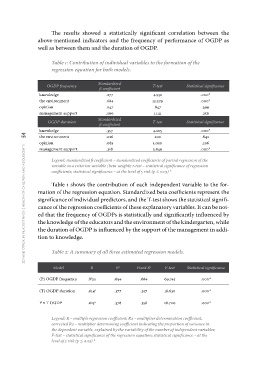
Table 1: Contribution of individual variables to the formation of the
regression equation for both models.
zdravje otrok in mladostnikov | health of children and adolescents 54 OGDP frequency Standardized T-test Statistical significance
ß coefficient
knowledge 4.551 .000*
the environment .277 12.379 .000*
opinion .684 .847 .399
management support .047 1.141 .256
.066
OGDP duration T-test Statistical significance
Standardized
knowledge ß coefficient 4.105 .000*
the environment .200 .842
opinion .357 1.050 .296
management support .016 3.840 .000*
.083
.318
Legend: standardized ß coefficient – standardized coefficients of partial regression of the
variable to a criterion variable (beta weight); t-test – statistical significance of regression
coefficients; statistical significance – at the level of 5 risk (p ≤ 0.05) *
Table 1 shows the contribution of each independent variable to the for-
mation of the regression equation. Standardized beta coefficients represent the
significance of individual predictors, and the T-test shows the statistical signifi-
cance of the regression coefficients of these explanatory variables. It can be not-
ed that the frequency of OGDPs is statistically and significantly influenced by
the knowledge of the educators and the environment of the kindergarten, while
the duration of OGDP is influenced by the support of the management in addi-
tion to knowledge.
Table 2: A summary of all three estimated regression models.
Model R R2 Fixed R2 F-test Statistical significance
(P) OGDP frequency .833a
(T) OGDP duration .614a .694 .684 69.745 .000*
P x T OGDP .615a
.377 .357 18.630 .000*
.378 .358 18.700 .000*
Legend: R – multiple regression coefficient; R2 – multiplier determination coefficient,
corrected R2 – multiplier determining coefficient indicating the proportion of variance in
the dependent variable, explained by the variability of the number of independent variables;
F-test – statistical significance of the regression equation; statistical significance – at the
level of 5 risk (p ≤ 0.05) *
above-mentioned indicators and the frequency of performance of OGDP as
well as between them and the duration of OGDP.
Table 1: Contribution of individual variables to the formation of the
regression equation for both models.
zdravje otrok in mladostnikov | health of children and adolescents 54 OGDP frequency Standardized T-test Statistical significance
ß coefficient
knowledge 4.551 .000*
the environment .277 12.379 .000*
opinion .684 .847 .399
management support .047 1.141 .256
.066
OGDP duration T-test Statistical significance
Standardized
knowledge ß coefficient 4.105 .000*
the environment .200 .842
opinion .357 1.050 .296
management support .016 3.840 .000*
.083
.318
Legend: standardized ß coefficient – standardized coefficients of partial regression of the
variable to a criterion variable (beta weight); t-test – statistical significance of regression
coefficients; statistical significance – at the level of 5 risk (p ≤ 0.05) *
Table 1 shows the contribution of each independent variable to the for-
mation of the regression equation. Standardized beta coefficients represent the
significance of individual predictors, and the T-test shows the statistical signifi-
cance of the regression coefficients of these explanatory variables. It can be not-
ed that the frequency of OGDPs is statistically and significantly influenced by
the knowledge of the educators and the environment of the kindergarten, while
the duration of OGDP is influenced by the support of the management in addi-
tion to knowledge.
Table 2: A summary of all three estimated regression models.
Model R R2 Fixed R2 F-test Statistical significance
(P) OGDP frequency .833a
(T) OGDP duration .614a .694 .684 69.745 .000*
P x T OGDP .615a
.377 .357 18.630 .000*
.378 .358 18.700 .000*
Legend: R – multiple regression coefficient; R2 – multiplier determination coefficient,
corrected R2 – multiplier determining coefficient indicating the proportion of variance in
the dependent variable, explained by the variability of the number of independent variables;
F-test – statistical significance of the regression equation; statistical significance – at the
level of 5 risk (p ≤ 0.05) *