Page 138 - Petelin, Ana. 2020. Ed. Zdravje delovno aktivne populacije / Health of the Working-Age Population. Proceedings. Koper: University of Primorska Press.
P. 138
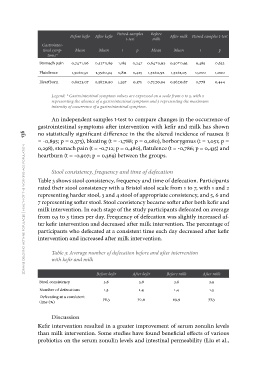
Before kefir After kefir Paired-samples Before After milk Paired samples t-test
t-test milk
Gastrointes- Mean Mean t p Mean Mean t p
tinal symp-
0,74±1,06 0,52±0,89 1,185 0,247 0,64±0,92 0,50±0,93 0,485 0,632
toms* 1,50±0,91 1,35±0,94 0,811 0,425 1,52±0,92 1,52±1,05 0,000 1,000
Stomach pain 0,89±1,07 0,58±0,90 1,397 0,175 0,72±0,94 0,56±0,87 0,778 0,444
Flatulence
Heartburn
zdravje delovno aktivne populacije | health of the working-age population 136 Legend: * Gastrointestinal symptom values are expressed on a scale from 0 to 5, with 0
representing the absence of a gastrointestinal symptom and 5 representing the maximum
intensity of occurrence of a gastrointestinal symptom.
An independent samples t-test to compare changes in the occurrence of
gastrointestinal symptoms after intervention with kefir and milk has shown
no statistically significant difference in the the altered incidence of nausea (t
= -0,895; p = 0,375), bloating (t = -1,788; p = 0,080), borborygmus (t = 1,051; p =
0,298), stomach pain (t = -0,712; p = 0,480), flatulence (t = -0,786; p = 0,435) and
heartburn (t = -0,907; p = 0,369) between the groups.
Stool consistency, frequency and time of defecation
Table 3 shows stool consistency, frequency and time of defecation. Participants
rated their stool consistency with a Bristol stool scale from 1 to 7, with 1 and 2
representing harder stool, 3 and 4 stool of appropriate consistency, and 5, 6 and
7 representing softer stool. Stool consistency became softer after both kefir and
milk intervention. In each stage of the study participants defecated on average
from 0,5 to 3 times per day. Frequency of defecation was slightly increased af-
ter kefir intervention and decreased after milk intervention. The percentage of
participants who defecated at a consistent time each day decreased after kefir
intervention and increased after milk intervention.
Table 3: Average number of defecation before and after intervention
with kefir and milk
Stool consistency Before kefir After kefir Before milk After milk
3,6 3,8 3,8 3,9
Number of defecations 1,3 1,4 1,4 1,3
Defecating at a consistent
time (%) 78,3 70,0 69,9 77,3
Discussion
Kefir intervention resulted in a greater improvement of serum zonulin levels
than milk intervention. Some studies have found beneficial effects of various
probiotics on the serum zonulin levels and intestinal permeability (Liu et al.,
t-test milk
Gastrointes- Mean Mean t p Mean Mean t p
tinal symp-
0,74±1,06 0,52±0,89 1,185 0,247 0,64±0,92 0,50±0,93 0,485 0,632
toms* 1,50±0,91 1,35±0,94 0,811 0,425 1,52±0,92 1,52±1,05 0,000 1,000
Stomach pain 0,89±1,07 0,58±0,90 1,397 0,175 0,72±0,94 0,56±0,87 0,778 0,444
Flatulence
Heartburn
zdravje delovno aktivne populacije | health of the working-age population 136 Legend: * Gastrointestinal symptom values are expressed on a scale from 0 to 5, with 0
representing the absence of a gastrointestinal symptom and 5 representing the maximum
intensity of occurrence of a gastrointestinal symptom.
An independent samples t-test to compare changes in the occurrence of
gastrointestinal symptoms after intervention with kefir and milk has shown
no statistically significant difference in the the altered incidence of nausea (t
= -0,895; p = 0,375), bloating (t = -1,788; p = 0,080), borborygmus (t = 1,051; p =
0,298), stomach pain (t = -0,712; p = 0,480), flatulence (t = -0,786; p = 0,435) and
heartburn (t = -0,907; p = 0,369) between the groups.
Stool consistency, frequency and time of defecation
Table 3 shows stool consistency, frequency and time of defecation. Participants
rated their stool consistency with a Bristol stool scale from 1 to 7, with 1 and 2
representing harder stool, 3 and 4 stool of appropriate consistency, and 5, 6 and
7 representing softer stool. Stool consistency became softer after both kefir and
milk intervention. In each stage of the study participants defecated on average
from 0,5 to 3 times per day. Frequency of defecation was slightly increased af-
ter kefir intervention and decreased after milk intervention. The percentage of
participants who defecated at a consistent time each day decreased after kefir
intervention and increased after milk intervention.
Table 3: Average number of defecation before and after intervention
with kefir and milk
Stool consistency Before kefir After kefir Before milk After milk
3,6 3,8 3,8 3,9
Number of defecations 1,3 1,4 1,4 1,3
Defecating at a consistent
time (%) 78,3 70,0 69,9 77,3
Discussion
Kefir intervention resulted in a greater improvement of serum zonulin levels
than milk intervention. Some studies have found beneficial effects of various
probiotics on the serum zonulin levels and intestinal permeability (Liu et al.,