Page 72 - Kutnar, Andreja, et al., eds., 2015. Proceedings of the 1st COST Action FP1307 International Conference - Life Cycle Assessment, EPDs, and modified wood. University of Primorska Press, Koper.
P. 72
results
showed
that
the
products
made
of
waste
wood
have
smaller
effect
on
the
environment
than
the
products
made
from
raw
materials.
Table
1
shows
results
of
LCA
analysis
of
particleboard
and
pellets
produced
from
raw
material
and
from
waste
wood.
For
both,
particleboard
and
pellets,
the
environmental
impacts
were
considerably
lower
in
case
of
products
made
of
waste
wood.
The
major
contribution
to
decreased
environmental
impacts
was
reduced
energy
use
for
drying
the
material
in
the
production
of
the
products
and
shorter
transportation
distances
of
the
input
material
to
the
manufacturing
facilities,
when
the
waste
wood
from
Port
of
Koper
is
used
to
produce
particleboards
and
pellets.
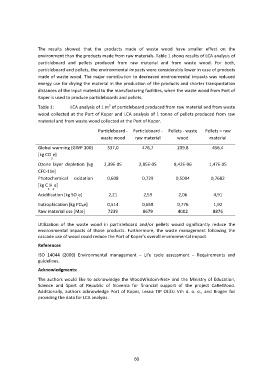
Table
1:
LCA
analysis
of
1
m3
of
particleboard
produced
from
raw
material
and
from
waste
wood
collected
at
the
Port
of
Koper
and
LCA
analysis
of
1
tonne
of
pellets
produced
from
raw
material
and
from
waste
wood
collected
at
the
Port
of
Koper.
Particleboard
-‐
Particleboard
-‐
Pellets
-‐
waste
Pellets
–
raw
waste
wood
raw
material
wood
material
Global
warming
(GWP
100)
337,0
476,7
209,8
456,4
[kg
CO e]
2
Ozone
layer
depletion
[kg
2,39E-‐05
2,85E-‐05
8,42E-‐06
1,47E-‐05
CFC-‐11e]
Photochemical
oxidation
0,608
0,729
0,5004
0,7682
[kg
C H e]
24
Acidification
[kg
SO e]
2,21
2,59
2,06
4,91
2
Eutrophication
[kg
PO₄e]
0,514
0,658
0,776
1,92
Raw
material
use
[MJe]
7239
8679
4002
8876
Utilization
of
the
waste
wood
in
particleboard
and/or
pellets
would
significantly
reduce
the
environmental
impacts
of
those
products.
Furthermore,
the
waste
management
following
the
cascade
use
of
wood
could
reduce
the
Port
of
Koper’s
overall
environmental
impact.
References
ISO
14044
(2006)
Environmental
management
–
Life
cycle
assessment
–
Requirements
and
guidelines.
Acknowledgments:
The
authors
would
like
to
acknowledge
the
WoodWisdom-‐Net+
and
the
Ministry
of
Education,
Science
and
Sport
of
Republic
of
Slovenia
for
financial
support
of
the
project
CaReWood.
Additionally,
authors
acknowledge
Port
of
Koper,
Lesna
TIP
Otiški
Vrh
d.
o.
o.,
and
Biogen
for
providing
the
data
for
LCA
analysis.
60
showed
that
the
products
made
of
waste
wood
have
smaller
effect
on
the
environment
than
the
products
made
from
raw
materials.
Table
1
shows
results
of
LCA
analysis
of
particleboard
and
pellets
produced
from
raw
material
and
from
waste
wood.
For
both,
particleboard
and
pellets,
the
environmental
impacts
were
considerably
lower
in
case
of
products
made
of
waste
wood.
The
major
contribution
to
decreased
environmental
impacts
was
reduced
energy
use
for
drying
the
material
in
the
production
of
the
products
and
shorter
transportation
distances
of
the
input
material
to
the
manufacturing
facilities,
when
the
waste
wood
from
Port
of
Koper
is
used
to
produce
particleboards
and
pellets.
Table
1:
LCA
analysis
of
1
m3
of
particleboard
produced
from
raw
material
and
from
waste
wood
collected
at
the
Port
of
Koper
and
LCA
analysis
of
1
tonne
of
pellets
produced
from
raw
material
and
from
waste
wood
collected
at
the
Port
of
Koper.
Particleboard
-‐
Particleboard
-‐
Pellets
-‐
waste
Pellets
–
raw
waste
wood
raw
material
wood
material
Global
warming
(GWP
100)
337,0
476,7
209,8
456,4
[kg
CO e]
2
Ozone
layer
depletion
[kg
2,39E-‐05
2,85E-‐05
8,42E-‐06
1,47E-‐05
CFC-‐11e]
Photochemical
oxidation
0,608
0,729
0,5004
0,7682
[kg
C H e]
24
Acidification
[kg
SO e]
2,21
2,59
2,06
4,91
2
Eutrophication
[kg
PO₄e]
0,514
0,658
0,776
1,92
Raw
material
use
[MJe]
7239
8679
4002
8876
Utilization
of
the
waste
wood
in
particleboard
and/or
pellets
would
significantly
reduce
the
environmental
impacts
of
those
products.
Furthermore,
the
waste
management
following
the
cascade
use
of
wood
could
reduce
the
Port
of
Koper’s
overall
environmental
impact.
References
ISO
14044
(2006)
Environmental
management
–
Life
cycle
assessment
–
Requirements
and
guidelines.
Acknowledgments:
The
authors
would
like
to
acknowledge
the
WoodWisdom-‐Net+
and
the
Ministry
of
Education,
Science
and
Sport
of
Republic
of
Slovenia
for
financial
support
of
the
project
CaReWood.
Additionally,
authors
acknowledge
Port
of
Koper,
Lesna
TIP
Otiški
Vrh
d.
o.
o.,
and
Biogen
for
providing
the
data
for
LCA
analysis.
60