Page 36 - Petelin, Ana, Nejc Šarabon, Boštjan Žvanut, eds. 2017. Zdravje delovno aktivne populacije ▪︎ Health of the Working-Age Population. Proceedings. Koper: Založba Univerze na Primorskem/University of Primorska Press
P. 36
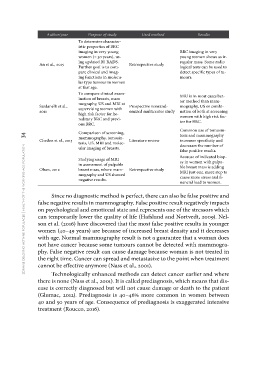
Author/year Purpose of study Used method Results
An et al., 2015 Retrospective study
To determine character- Prospective nonrand- BRC imaging in very
Sardanelli et al., istic properties of BRC omized multicenter study young women shows as ir-
2011 imaging in very young regular mass. Some radio-
Chetlen et al., 2015 women (< 30 years), us- logical tests can be used to
Olsen, 2012 ing updated BI-RADS. detect specific types of tu-
Further goal is to com- mours.
pare clinical and imag-
ing functions in molecu- MRI is in most cases bet-
lar type tumour in women ter method than mam-
at that age. mography, US or combi-
To compare clinical exam- nation of both at screening
ination of breasts, mam- women with high risk fac-
mography, US and MRI at tor for BRC.
supervising women with Common use of tomosin-
high risk factor for he- tesis and mammography
reditary BRC and previ- increases specificity and
ous BRC. decreases the number of
false positive results.
zdravje delovno aktivne populacije | health of the working-age population 34 Comparison of screening, Literature review Because of indicated biop-
mammography, tomosin- sy in women with palpa-
tesis, US, MRI and molec- ble breast mass is adding
ular imaging of breasts. MRI just one. more step to
cause more stress and fi-
Studying usage of MRI Retrospective study nancial load to women.
in assessment of palpable
breast mass, where mam-
mography and US showed
negative results.
Since no diagnostic method is perfect, there can also be false positive and
false negative results in mammography. False positive result negatively impacts
on psychological and emotional state and represents one of the stressors which
can temporarily lower the quality of life (Hafslund and Nortvedt, 2009). Nel-
son et al. (2016) have discovered that the most false positive results in younger
women (40–49 years) are because of increased breast density and it decreases
with age. Normal mammography result is not a guarantee that a woman does
not have cancer because some tumours cannot be detected with mammogra-
phy. False negative result can cause damage because woman is not treated in
the right time. Cancer can spread and metastasize to the point when treatment
cannot be effective anymore (Nass et al., 2001).
Technologically enhanced methods can detect cancer earlier and where
there is none (Nass et al., 2001). It is called prediagnosis, which means that dis-
ease is correctly diagnosed but will not cause damage or death to the patient
(Glumac, 2012). Prediagnosis is 40–46% more common in women between
40 and 50 years of age. Consequence of prediagnosis is exaggerated intensive
treatment (Roucco, 2016).
An et al., 2015 Retrospective study
To determine character- Prospective nonrand- BRC imaging in very
Sardanelli et al., istic properties of BRC omized multicenter study young women shows as ir-
2011 imaging in very young regular mass. Some radio-
Chetlen et al., 2015 women (< 30 years), us- logical tests can be used to
Olsen, 2012 ing updated BI-RADS. detect specific types of tu-
Further goal is to com- mours.
pare clinical and imag-
ing functions in molecu- MRI is in most cases bet-
lar type tumour in women ter method than mam-
at that age. mography, US or combi-
To compare clinical exam- nation of both at screening
ination of breasts, mam- women with high risk fac-
mography, US and MRI at tor for BRC.
supervising women with Common use of tomosin-
high risk factor for he- tesis and mammography
reditary BRC and previ- increases specificity and
ous BRC. decreases the number of
false positive results.
zdravje delovno aktivne populacije | health of the working-age population 34 Comparison of screening, Literature review Because of indicated biop-
mammography, tomosin- sy in women with palpa-
tesis, US, MRI and molec- ble breast mass is adding
ular imaging of breasts. MRI just one. more step to
cause more stress and fi-
Studying usage of MRI Retrospective study nancial load to women.
in assessment of palpable
breast mass, where mam-
mography and US showed
negative results.
Since no diagnostic method is perfect, there can also be false positive and
false negative results in mammography. False positive result negatively impacts
on psychological and emotional state and represents one of the stressors which
can temporarily lower the quality of life (Hafslund and Nortvedt, 2009). Nel-
son et al. (2016) have discovered that the most false positive results in younger
women (40–49 years) are because of increased breast density and it decreases
with age. Normal mammography result is not a guarantee that a woman does
not have cancer because some tumours cannot be detected with mammogra-
phy. False negative result can cause damage because woman is not treated in
the right time. Cancer can spread and metastasize to the point when treatment
cannot be effective anymore (Nass et al., 2001).
Technologically enhanced methods can detect cancer earlier and where
there is none (Nass et al., 2001). It is called prediagnosis, which means that dis-
ease is correctly diagnosed but will not cause damage or death to the patient
(Glumac, 2012). Prediagnosis is 40–46% more common in women between
40 and 50 years of age. Consequence of prediagnosis is exaggerated intensive
treatment (Roucco, 2016).