Page 103 - Glasbenopedagoški zbornik Akademije za glasbo v Ljubljani
P. 103
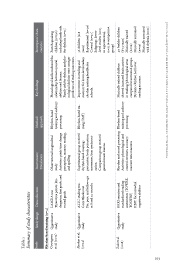
Participants’ chara- cteristics French-speaking children (n=130) including family risk for dyslexia (n=31) 56 children (6-8 years) Experimental (n=29) Control (n=27) Subgroup: lower- -level readers (n=15 in experimental, n=12 in comparison group) 40 healthy children (6-13 years) Musically trained (n=16) Musicall
Phonological skills mediated the relationship between musical Family risk for dyslexia and pho- nological abilities were stronger predictors of reading outcomes. Improvement in reading and memory for lower-level readers, rhythm training feasible for Musically trained children showed increased brain activity in reading/pho
Key findings abilities and literacy. schools. reading accuracy. Jovana Blagojević ◆ THE EFFECTS OF MUSICAL STIMULATION ON CHILDREN WITH DYSLEXIA
Method/ approach Rhythm-based training and auditory processing Rhythm-based tra- ining (Orff ) Rhythm-based training and auditory processing
Observational longitudinal Activities: pitch/time change perception, memory, reading, Experimental group received rhythm-based training: percussion, body percussion, movement, beat synchroni- Comparison group received Rhythm and sound processing Activities: phonological and control exercises, accuracy/ reaction time
Intervention/ Stimulation study and spelling zation. general music lessons.
Summary of study characteristics Data collection Study design Rhythm-based training (n=4) LAMDA test Quantitative Three time points: kin- study dergarten, first grade, and second grade ALLU reading test. Quantitative Corsi Blocks test study Pre, post, and follow-ups at 8 and 20 months fMRI exercises and Quantitative standar
Table 2 Study Couvignou et al. (2023) Ahokas et al. (2024) Zuk et al. (2018)
103