Page 105 - Glasbenopedagoški zbornik Akademije za glasbo v Ljubljani
P. 105
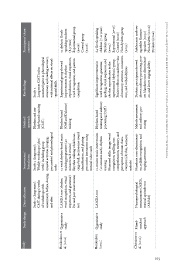
Participants’ chara- cteristics Dyslexic Italian-spea- reading skills, but the music group king children (n=48) 8-11 years Experimental group (n=24) Control group (n=24) Children and ado- lescents with reading difficulties Elementary school students with diagno- 34 participants Experimental group - dyslexic children (n=12) Control grou
Key findings Rhythm-based training Both groups improved in general showed greater gains in reading accuracy and phonological awareness. Combined interventions imp- roved reading and phonological skills more than single interven- tions. Combined interventions imp- roved reading and writing skills; highlighted the need for a holistic sed dyslexia
Method/ approach (Kodaly and Orff ) Rhythm and melody- -based training and auditory processing Rhythm and melody- -based training with digital technologies Rhythm-based tra- ining (CMT) Method/ approach Rhythm and me- lody-based training (CMT) Rhythm based (Orff and Dalcroze) training Rhythm-based training and auditory processing
1. Experimental group: rhythm syllables, body movement with Training sessions 1 hour, 2 a week (30 weeks in total) 2. Control group: painting lessons (creativity and fine 1. Auditory (phoneme pro- cessing, non-speech rhythm) 2. Music (rhythm, singing, 3.Combined music/auditory rhythm patterns, intonation, 2.T echnological tools (voiceo- ve
Intervention/ Stimulation sessments and phonological training (percussion, rhythm music) motor skills) clapping, percussion) and reading Review of 31 studies focused 1.Music exercises (tapping, pitch variation) Study 1 (short term): Intervention/ Stimulation Study 2 (long term): week) including group tasks minutes each session) musical val
Data collection Cognitive ability as- tasks Pre and post intervention assessments Systematic review – rhythm and melody-based training (n=2) 18 studies reviewed inclu- ding intervention types: au- ditory processing training, music training, combined interventions on music-based and digital technology-integrated interventions for dyslexic
Study design Quantitative study Systematic review Systematic revi- T odino (2023) ew (PRISMA- -ScR) Rhythm and melody-based training (n=4) Mixed-metho- ds approach Study design Quantitative study Quantitative study Mixed- -method approach
Flaugnacco et Cancer and Antonietti Di Paolo and Habib et al. Bouloukou et Bouloukou Christiner et
Study al. (2015) (2022) (2016) Study al. (2021) (2022) al. (2022)
105