Page 91 - Rižnar, Igor, and Klemen Kavčič (ed.). 2017. Connecting Higher Education Institutions with Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises. Koper: University of Primorska Press
P. 91
Maturity of Project Management in Slovenian Companies
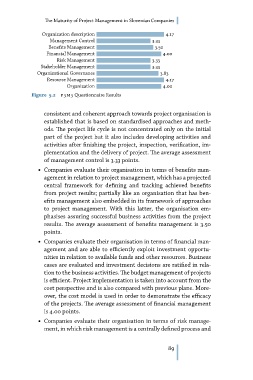
Organization description 4.17
Management Control 3.33
Benefits Management
3.50
Financial Management 4.00
Risk Management
3.33
Stakeholder Management 3.33
Organizational Governance
3.83
Resource Management 4.17
Organization
4.00
Figure 5.2 p3 m3 Questionnaire Results
consistent and coherent approach towards project organisation is
established that is based on standardised approaches and meth-
ods. The project life cycle is not concentrated only on the initial
part of the project but it also includes developing activities and
activities after finishing the project, inspection, verification, im-
plementation and the delivery of project. The average assessment
of management control is 3.33 points.
• Companies evaluate their organisation in terms of benefits man-
agement in relation to project management, which has a projected
central framework for defining and tracking achieved benefits
from project results; partially like an organisation that has ben-
efits management also embedded in its framework of approaches
to project management. With this latter, the organisation em-
phasises assuring successful business activities from the project
results. The average assessment of benefits management is 3.50
points.
• Companies evaluate their organisation in terms of financial man-
agement and are able to efficiently exploit investment opportu-
nities in relation to available funds and other resources. Business
cases are evaluated and investment decisions are ratified in rela-
tion to the business activities. The budget management of projects
is efficient. Project implementation is taken into account from the
cost perspective and is also compared with previous plans. More-
over, the cost model is used in order to demonstrate the efficacy
of the projects. The average assessment of financial management
is 4.00 points.
• Companies evaluate their organisation in terms of risk manage-
ment, in which risk management is a centrally defined process and
89
Organization description 4.17
Management Control 3.33
Benefits Management
3.50
Financial Management 4.00
Risk Management
3.33
Stakeholder Management 3.33
Organizational Governance
3.83
Resource Management 4.17
Organization
4.00
Figure 5.2 p3 m3 Questionnaire Results
consistent and coherent approach towards project organisation is
established that is based on standardised approaches and meth-
ods. The project life cycle is not concentrated only on the initial
part of the project but it also includes developing activities and
activities after finishing the project, inspection, verification, im-
plementation and the delivery of project. The average assessment
of management control is 3.33 points.
• Companies evaluate their organisation in terms of benefits man-
agement in relation to project management, which has a projected
central framework for defining and tracking achieved benefits
from project results; partially like an organisation that has ben-
efits management also embedded in its framework of approaches
to project management. With this latter, the organisation em-
phasises assuring successful business activities from the project
results. The average assessment of benefits management is 3.50
points.
• Companies evaluate their organisation in terms of financial man-
agement and are able to efficiently exploit investment opportu-
nities in relation to available funds and other resources. Business
cases are evaluated and investment decisions are ratified in rela-
tion to the business activities. The budget management of projects
is efficient. Project implementation is taken into account from the
cost perspective and is also compared with previous plans. More-
over, the cost model is used in order to demonstrate the efficacy
of the projects. The average assessment of financial management
is 4.00 points.
• Companies evaluate their organisation in terms of risk manage-
ment, in which risk management is a centrally defined process and
89