Page 188 - Hojnik, Jana. 2017. In Persuit of Eco-innovation. Drivers and Consequences of Eco-innovation at Firm Level. Koper: University of Primorska Press
P. 188
Pursuit of Eco-innovation
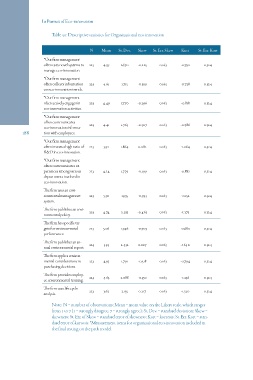
Table 50: Descriptive statistics for Organizational eco-innovation
N Mean St. Dev. Skew St. Err. Skew Kurt St. Err. Kurt
*Our firm management 4.39 1.670 -0.225 0.163 -0.792 0.324
often uses novel systems to 223
manage eco-innovation.
*Our firm management 223 4.61 1.715 -0.399 0.163 -0.728 0.324
often collects information
on eco-innovation trends.
*Our firm management
often actively engages in 223 4.49 1.770 -0.296 0.163 -0.818 0.324
eco-innovation activities.
*Our firm management
often communicates 223 4.41 1.763 -0.307 0.163 -0.786 0.324
eco-innovation informa-
188 tion with employees.
*Our firm management 3.92 1.864 0.082 0.163 -1.064 0.324
often invests a high ratio of 223
R&D in eco-innovation.
*Our firm management 1.779 -0.199 0.163 -0.882 0.324
often communicates ex-
periences among various 223 4.24
departments involved in
eco-innovation.
The firm uses an envi-
ronmental management 223 5.30 1.935 -0.993 0.163 -0.152 0.324
system.
The firm publishes an envi- 223 4.74 2.233 -0.463 0.163 -1.273 0.324
ronmental policy.
The firm has specific tar-
gets for environmental 223 5.06 1.946 -0.703 0.163 -0.680 0.324
performance.
The firm publishes an an- 223 3.93 2.432 0.027 0.163 -1.640 0.324
nual environmental report.
The firm applies environ-
mental considerations to 223 4.95 1.791 -0.518 0.163 -0.794 0.324
purchasing decisions.
The firm provides employ- 223 4.63 2.088 -0.350 0.163 -1.236 0.324
ee environmental training.
The firm uses life cycle 223 3.62 2.135 0.217 0.163 -1.320 0.324
analysis.
Note: N = number of observations; Mean = mean value on the Likert scale, which ranges
from 1 to 7 (1 = strongly disagree, 7 = strongly agree); St. Dev. = standard deviation; Skew =
skewness; St. Err. of Skew = standard error of skewness; Kurt = kurtosis; St. Err. Kurt = stan-
dard error of kurtosis. *Measurement items for organizational eco-innovation included in
the final testing on the path model.
Table 50: Descriptive statistics for Organizational eco-innovation
N Mean St. Dev. Skew St. Err. Skew Kurt St. Err. Kurt
*Our firm management 4.39 1.670 -0.225 0.163 -0.792 0.324
often uses novel systems to 223
manage eco-innovation.
*Our firm management 223 4.61 1.715 -0.399 0.163 -0.728 0.324
often collects information
on eco-innovation trends.
*Our firm management
often actively engages in 223 4.49 1.770 -0.296 0.163 -0.818 0.324
eco-innovation activities.
*Our firm management
often communicates 223 4.41 1.763 -0.307 0.163 -0.786 0.324
eco-innovation informa-
188 tion with employees.
*Our firm management 3.92 1.864 0.082 0.163 -1.064 0.324
often invests a high ratio of 223
R&D in eco-innovation.
*Our firm management 1.779 -0.199 0.163 -0.882 0.324
often communicates ex-
periences among various 223 4.24
departments involved in
eco-innovation.
The firm uses an envi-
ronmental management 223 5.30 1.935 -0.993 0.163 -0.152 0.324
system.
The firm publishes an envi- 223 4.74 2.233 -0.463 0.163 -1.273 0.324
ronmental policy.
The firm has specific tar-
gets for environmental 223 5.06 1.946 -0.703 0.163 -0.680 0.324
performance.
The firm publishes an an- 223 3.93 2.432 0.027 0.163 -1.640 0.324
nual environmental report.
The firm applies environ-
mental considerations to 223 4.95 1.791 -0.518 0.163 -0.794 0.324
purchasing decisions.
The firm provides employ- 223 4.63 2.088 -0.350 0.163 -1.236 0.324
ee environmental training.
The firm uses life cycle 223 3.62 2.135 0.217 0.163 -1.320 0.324
analysis.
Note: N = number of observations; Mean = mean value on the Likert scale, which ranges
from 1 to 7 (1 = strongly disagree, 7 = strongly agree); St. Dev. = standard deviation; Skew =
skewness; St. Err. of Skew = standard error of skewness; Kurt = kurtosis; St. Err. Kurt = stan-
dard error of kurtosis. *Measurement items for organizational eco-innovation included in
the final testing on the path model.